HOW TO SELECT THE
PERFECT DIAMOND
Diamonds
Are you looking for the perfect diamond to say I do? The process of selecting a diamond and designing a ring or other jewellery item may seem overwhelming, but it doesn't have to be.
With Pearl and Diamond Designs, this can be an exciting and joyous experience where we help you to find the perfect stone for the perfect person.
Diamonds come in many different sizes, shapes, colours, and with various internal characteristics. Just like fingerprints, every single diamond is unique.
The 4 most important factors that influence the quality and price of diamonds are clarity, colour, cut and carat weight. Also known as the 4 Cs, these terms have become part of the international language that jewellery professionals use to describe and evaluate diamonds. The scarcity of each of the 4 Cs also has an impact on the value.
Diamond Quality Factors
The human contribution to a diamond’s beauty is a well-executed cut.
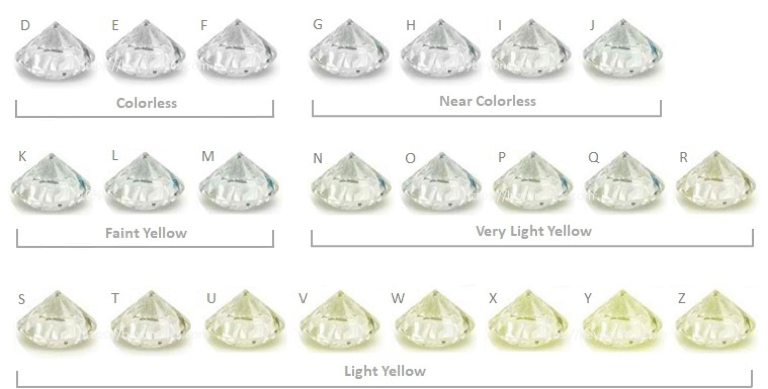
COLOUR
COLOUR
The less colour, the higher the grade. Even the slightest hint can make a dramatic difference in value.
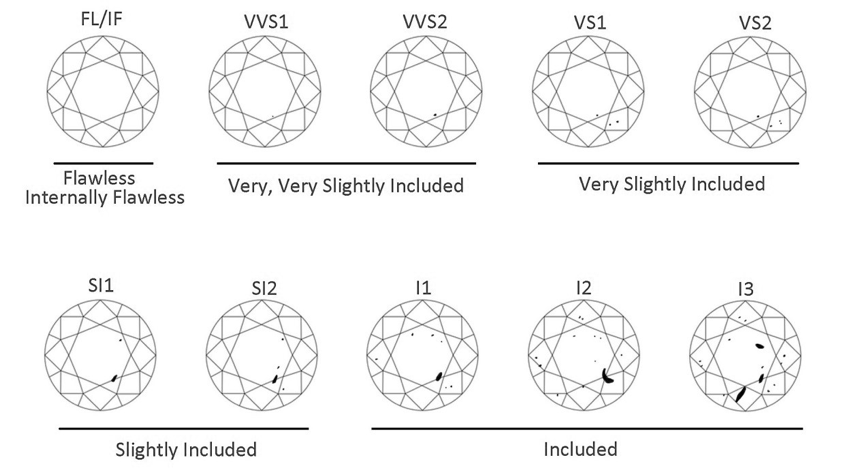
CLARITY
CLARITY
Clarity grades assess the number, size, relief, and position of inclusions and blemishes.
CUT
CUT
Cut (proportions, symmetry, and polish) is a measure of how a diamond’s facets interact with light.
CARAT WEIGHT
CARAT WEIGHT
Rarity means larger diamonds of the same quality are worth more per carat.
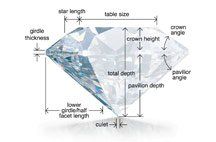
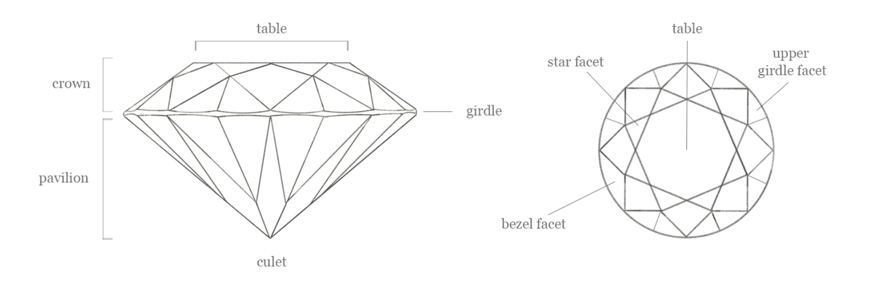
Diamond Cut
Whilst diamonds can be fashioned into different shapes, a diamond's cut grade is a measure of a diamond's light performance. In other words, it determines the diamond’s "sparkle". When a diamond is cut with the ideal proportions, light reflects out of the top of the diamond. If the diamond cut is too shallow, light escapes out of the bottom; too deep and it sneaks out the sides.
The most popular shape is round brilliant. Other popular shapes include oval, cushion, pear and princess brilliant cut. The shape of the diamond will determine the style of your ring or jewellery item.
Diamond Colour
Subtle differences in the colour of diamonds will have a dramatic effect on the value. Traditionally, a diamond's value is determined by the absence of colour, given that colour usually manifests as pale yellow in a diamond. Diamonds with less colour are scarcer. The exception is diamonds with intense colours, called fancy diamonds. Colour grading starts at D (colourless) and moves up the alphabet, increasing in yellowy hues as it escalates.
At Pearl and Diamond Designs, we use only colourless or near colourless diamonds for jewellery items that contain diamonds 0.2ct and smaller. This ensures that the jewellery item is top quality and has enough sparkle. In the case of larger diamonds, the colour depends on the specific diamond and on your budget.
Diamond Clarity
Clarity refers to the tiny, natural imperfections that are present in all but the rarest diamonds. Nearly all diamonds contain unique internal characteristics called inclusions and external characteristics called blemishes. Inclusions and blemishes are the natural results of a diamond's formation deep within the earth under extreme heat and pressure. The less inclusions, the better the clarity, the scarcer the diamond and the higher the value.
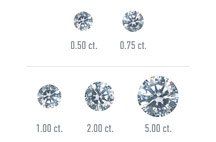
Diamond Carat
Carat weight is the most well-known and most misunderstood characteristic of the 4 Cs. It actually refers to the diamond's weight, not its size. A diamond's cut impacts how large the carat weight will appear. Smaller carat weight diamonds will appear larger with higher cut grades.
All else being equal, a diamond’s price increases with its carat weight, because larger diamonds are rarer and more desirable. However, two diamonds of equal carat weight can have very different values (and prices) depending on the colour, clarity and cut.
To maximise your budget, consider purchasing a diamond that is slightly below your ideal carat weight, as the prices of diamonds increase in brackets. For example, instead of a 2.0 carat diamond consider buying a 1.9 carat diamond.
Where to Start
You Might Like
4C's
Brouchure - PDF
Gem Cleaning
Gem Cleaning
Brouchure - PDF
Natural vs Synthetic
Brouchure - PDF